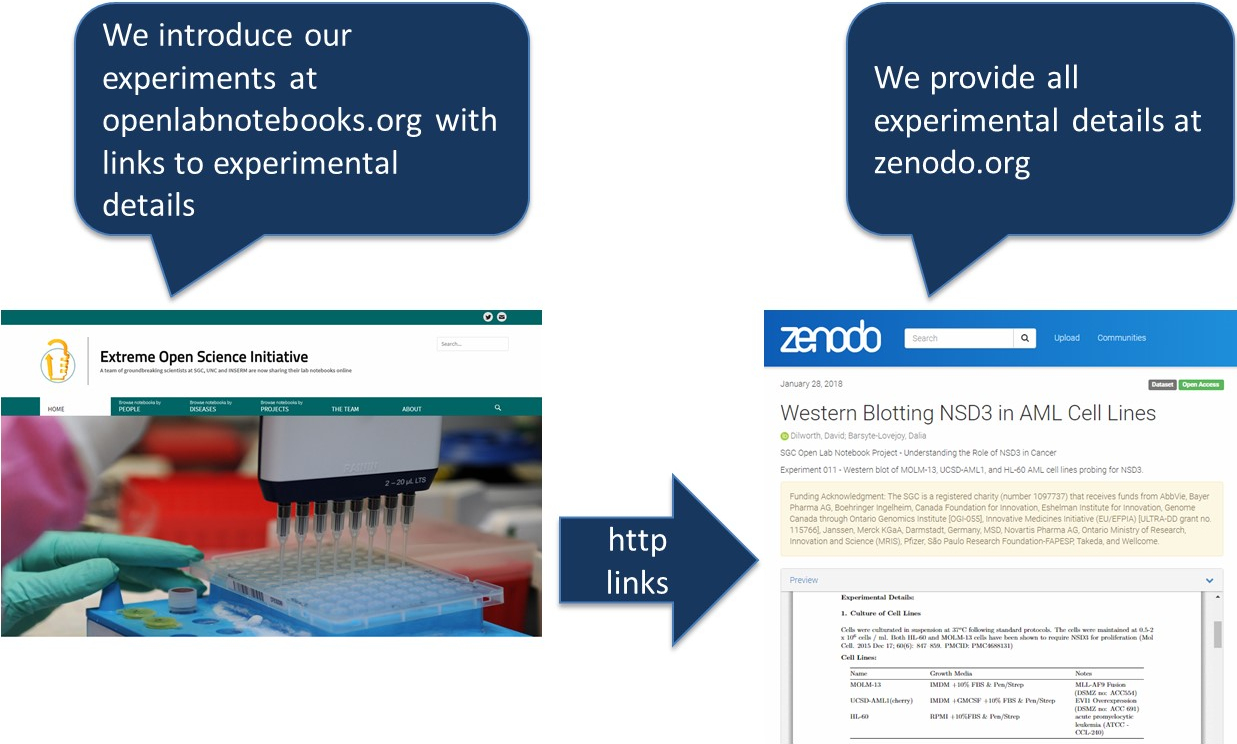
In a groundbreaking initiative, scientists around the world from Universities in Canada, France, Sweden, the UK, and the USA are starting to share their laboratory notebooks live, online. We believe that making our research, data, and protocols available on a day-to-day basis will generate scientific ideas and discussions, avoid redundancy, foster collaborations, and accelerate progress. Our hope is that this initiative will inspire others to follow. Join us!