Background
SMYD3 (SET and MYND domain containing protein 3) is a member of the SMYD lysine methylase family and plays an important role in lysine methylation of various histone and non-histone proteins such as H2A.Z.1-K101, VEDFR1-K831, MAP3K2-K260, HER2-K175 or AKT1-K14. SMYD3 is overexpressed in numerous human tumors and is a potential therapeutic target and prognostic factor in various solid cancers. (PIMID: 31935919).
Assay validation
SMYD3 has been reported to trimethylate MAP3K2 at lysine 260, which for the first time linked lysine methylation to Ras-driven signaling pathways in cancer (PIMID: 24847881). Based on the findings, we developed SMYD3 cellular assay in which exogenous HA-tagged MAP3K2 is methylated by exogenous SMYD3 in the HeLa cervical cancer cell line (Fig.1). Overexpression of SMYD3 but not its catalytic mutant (ΔNHSCDPN, Fig.1) increased MAP3K2-K260me3 levels (Fig.2). The assay was further validated with SMYD3 selective inhibitors EPZ031686 and BAY-6035. Both inhibitors decreased SMYD3 dependent exogenous MAP3K2-K260 trimethylation in a dose-dependent manner (Fig.3). The Z factor for the assay equals 0.86.
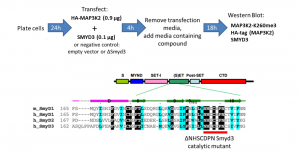
Fig.1. Assay schematic. Modified from (PIMID:20943667).

Fig.2. The wild type but not catalytic mutant of SMYD3 (ΔNHSCDPN) trimethylated MAP3K2-K260. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with empty vector (control), SMYD3 wild type or catalytic mutant (ΔSMYD3), and HA-tagged MAP3K2 for 24 h. The methylation levels were analyzed in Western Blot. (Shawna Organ)
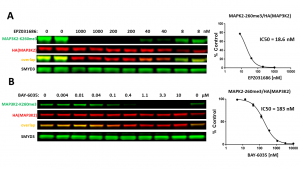 Fig.3. SMYD3 selective inhibitors decreased SMYD3 dependent MAP3K2-K260 trimethylation in a dose-dependent manner in cells. HeLa cells were co-transfected with SMYD3 and HA-tagged MAP3K2 and treated with EPZ031686 (A) and BAY-6035 (B) for 20 h. MAP3K2-K260me3 levels were determined by Western blot. The graphs represent the nonlinear fits of MAP3K2-K260me3 signal intensities normalized to HA(MAP3K2). The results are mean +/- SEM of 2 (A) and 3 (B) technical replicates. (Shawna Organ, Magdalena Szewczyk)
Fig.3. SMYD3 selective inhibitors decreased SMYD3 dependent MAP3K2-K260 trimethylation in a dose-dependent manner in cells. HeLa cells were co-transfected with SMYD3 and HA-tagged MAP3K2 and treated with EPZ031686 (A) and BAY-6035 (B) for 20 h. MAP3K2-K260me3 levels were determined by Western blot. The graphs represent the nonlinear fits of MAP3K2-K260me3 signal intensities normalized to HA(MAP3K2). The results are mean +/- SEM of 2 (A) and 3 (B) technical replicates. (Shawna Organ, Magdalena Szewczyk)
Experimental details are posted on Zenodo.
