Background
PRMT5 in complex with the WD-repeat protein MEP50 is the major type II protein arginine methyltransferase responsible for mono- and symmetric dimethylation of arginine in a great variety of proteins (Fig.1). It plays a critical role in diverse cellular processes such as genome organization, transcription, translation, differentiation, cell cycle, DNA repair, RNA processing, and metabolism (PMID:25662273). PRMT5 expression levels and methyltransferase activity were found to be dysregulated in a variety of cancers (PMID: 25662273).
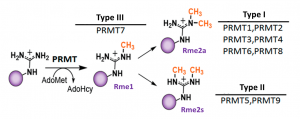
Fig.1. Mammalian PRMTs. There are 9 members and 3 types of the PRMT family. Type I, II and III PRMTs catalyze the formation of monomethyl arginines (Rme1). Type I PRMTs catalyze asymmetric arginine methylation (Rme2a), while type II PRMTs form symmetric arginine methylation (Rme2s). Type III PRMT can only monomethylate arginine residues. Modified from (PMID:29378138).
Assay validation
It has been reported previously, that the various SMN complex proteins, including SmBB’ are PRMT5 substrates (PMID:19520849). We found that the knocking down of PRMT5, but not PRMT1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 resulted in decreased SmBB’ symmetric dimethylation levels (Fig.2). PRMT9, another type II PRMT, is also not affecting SmBB’ Rme2s levels (PIMID: 25737013). The assay was further validated by treatment with selective PRMT5 chemical probe, GSK591. GSK591 decreased SmBB’-Rme2s levels in a dose-dependent manner (Fig.3). The assay was also used to validate the cellular activity of another PRMT5 selective chemical probe LLY-283 (PMID:30034588). Similar results were obtained with different cell lines (data not shown).
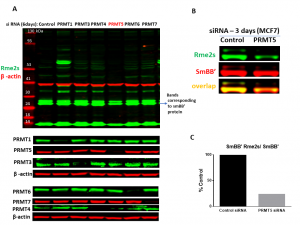
Fig.2. PRMT5 knock-down results in decrease in SmBB’-Rme2s levels. MCF7 cells were treated with siRNA targeted for different PRMTs and control siRNA for 6 (A) and 3 (B) days. A. Western blot analysis with an antibody recognizing symmetric arginine methylation (Rme2s) of various proteins. PRMTs expression after knock-down (KD) and β-actin controls are shown. Note that the loss of PTMT1 leads to decrease of Rme2a modification and the shared substrates become targets for PRMT5 leading to increase in Rme2s levels.B. Western blot analysis of the SmBB’-Rme2s levels after PRMT5 KD. C. Quantification of signal intensities of SmBB’-Rme2s normalized to total SmBB’ (n=1).
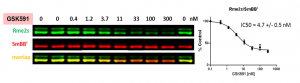
Fig.3. PRMT5 chemical probe, GSK591, decreases SmBB’ symmetric dimethylation in a dose-dependent manner. MCF7 cells were treated with inhibitor at indicated concentrations for 48 h and SmBB’-Rme2s and total SmBB’ levels were determined by Western blot. The graph represents nonlinear fits of SmBB’-Rme2s signal intensities normalized to total SmBB’. The results are mean +/- SEM of 3 replicates. The Z factor for the assay equals 0.67 (n=3).
Please visit Zenodo for experimental details.
