Background
HSP70 heat-shock proteins family, including constitutively expressed HSPA8 variant, facilitate correct folding of client proteins and degradation of unfolded clients. To achieve folding or degradation of client proteins, HSP70 cooperates with co-chaperones, which mostly bind to the highly conserved sequence EEVD in the C-terminal domain of HSP70 via their tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domain (PMID: 26565746). STIP1(HOP) and ubiquitin ligase STUB1(CHIP) and are TPR-containing co-chaperones that assist with protein folding or degradation, respectively (PIMID:22824801). It was shown previously that mutations within TPR domains of STIP1 (K8A) and STUB1 (K30A) abolished their interaction with HSPA8 (PIMID: 23865999, 26565746).
Assay validation
Assay measuring the interaction of HSPA8 to STIP1 and STUB1 co-chaperons was developed using NanoBRET technology – a proximity-based assay that can detect protein interactions by measuring energy transfer from a bioluminescent protein donor to a fluorescent protein acceptor. At the beginning we determined the optimal tag orientation and donor to acceptor ratio of donor constructs: N or C-terminally NanoLuc® tagged STIP1/STIP1 K8A mutant or STUB1/STUB1 K30A and acceptor construct: C-terminally HaloTag®Fusion tagged HSPA8. The best results were obtained with C-terminally tagged donor constructs and 1:9 donor to acceptor ratio. Consistent with previous findings the interaction (NanoBRET ratio) of HSPA8 and mutated co-chaperons was significantly lower compared to wild type proteins (Fig.1).
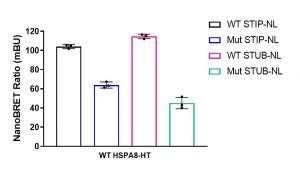
Fig.1. HSPA8 interaction with STIP1 (HOP) and STUB1 (CHIP) co-chaperones. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with Nanoluc (NL)-tagged STIP1 (WT or K8A mutant) or NL-tagged STUB1 (WT or K30A mutant) and Halo-tagged (HT) HSPA8 for 24 h. The interaction was measured using NanoBRET assay. The results are MEAN+/-SD of 3 technical replicates.
Experimental details are posted on Zenodo.
