Background:
I have been characterising the cellular potency of many M4K compounds against ALK2 and ALK5. Compounds that targets ALK2 and not ALK5 should be further evaluated for their ability to reduce the viability of cells derived from DIPG patients. Although these cultured cells might not reflect what actually happens in a DIPG patient’s brain, it is the the best tool we have on hand.
Viability assay using Celltiter Glo kit has been chosen as the main method for evaluating the efficacy of ALK2 inhibitors on DIPG patient-derived cells due to its robustness (refer to my previous post for how I determined this). As a pilot experiment, 8 ALK2 inhibitors with differing potencies were chosen and evaluated in 3 DIPG patient-derived cell lines (one with wild-type ALK2 and two with mutant ALK2).
Experimental design:
DIPG cells will be seeded into wells coated with laminin at densities optimised in previous experiments. After allowing the cells to adhere overnight, they will be treated with serial dilutions of various M4K compounds. After 7 days of compound treatment, the area occupied by the cells, the intensity of propidium iodide signal and Celltiter Glo luminescence signal will be determined.
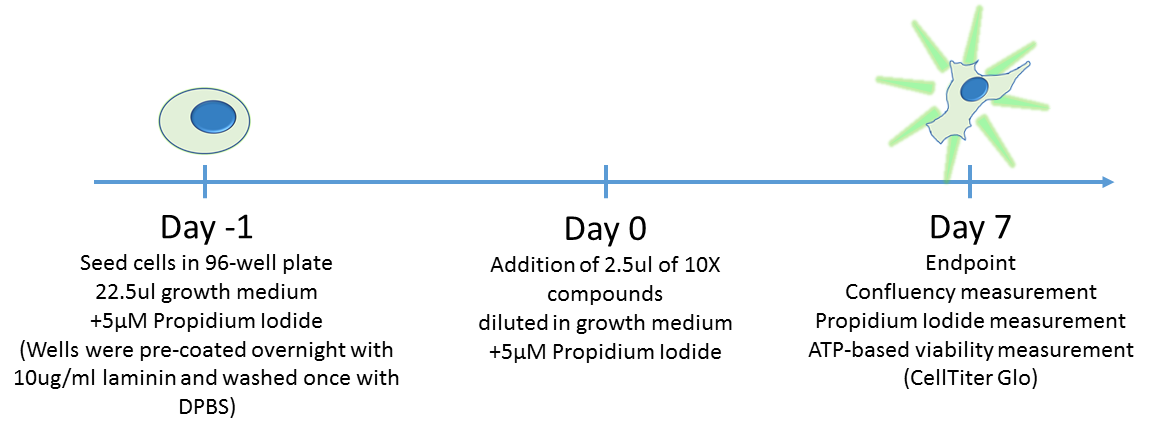
The timeline of this experiment
Results:
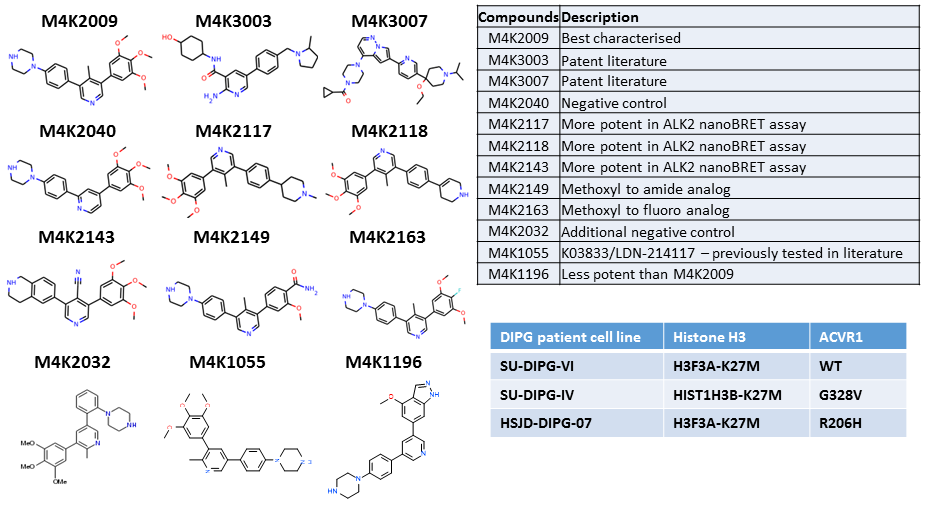
Chemical structures of the compounds tested in this experiment as well as the reasons they were selected (top table). The histone H3 and ACVR1/ALK2 mutation status of the different DIPG patient-derived cell lines is shown in bottom table.
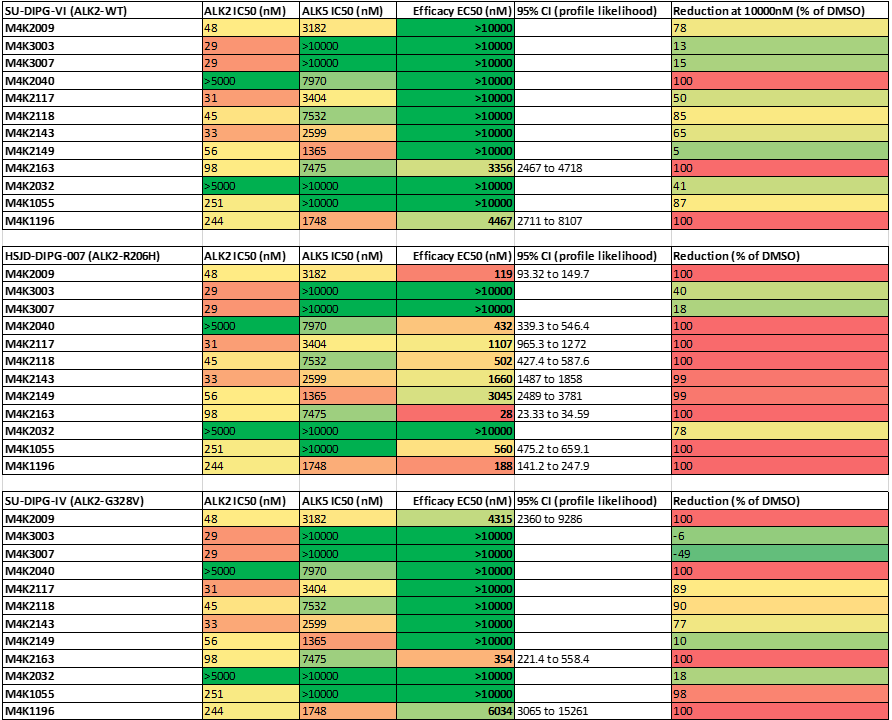
Efficacy of the compounds assayed compounds. EC50, 95% confidence interval of the EC50 values and maximal observed reduction in viability are shown for each compounds.
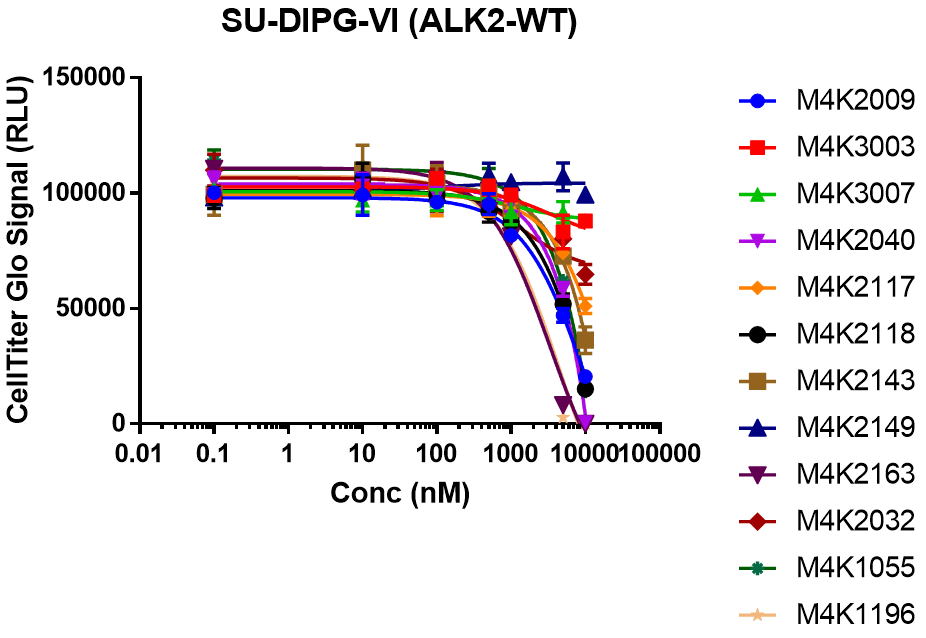
EC50 curves for SU-DIPG-VI cells treated with dilution series of each compound for 7 days.
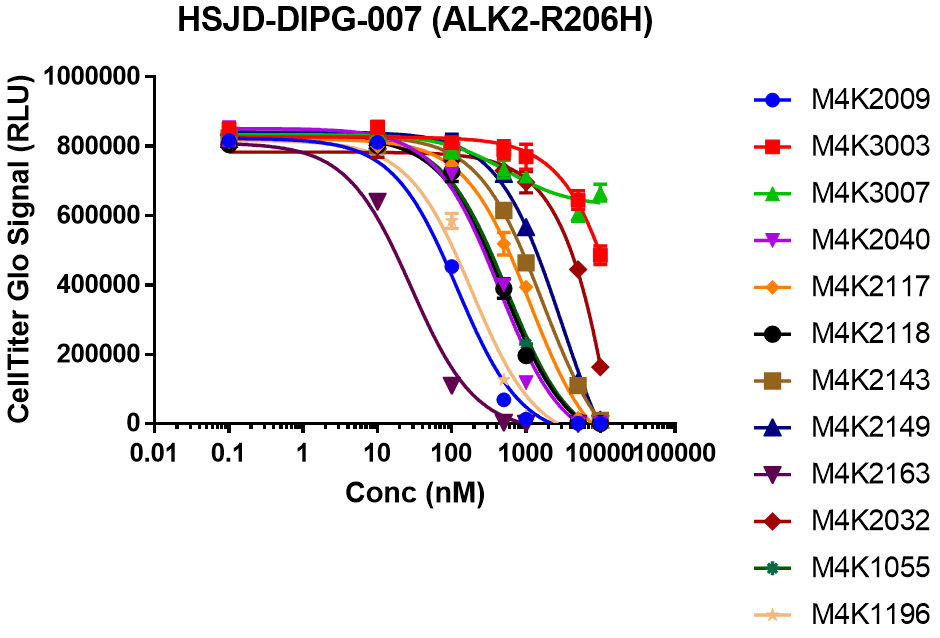
EC50 curves for HSJD-DIPG-007 cells treated with dilution series of each compound for 7 days.
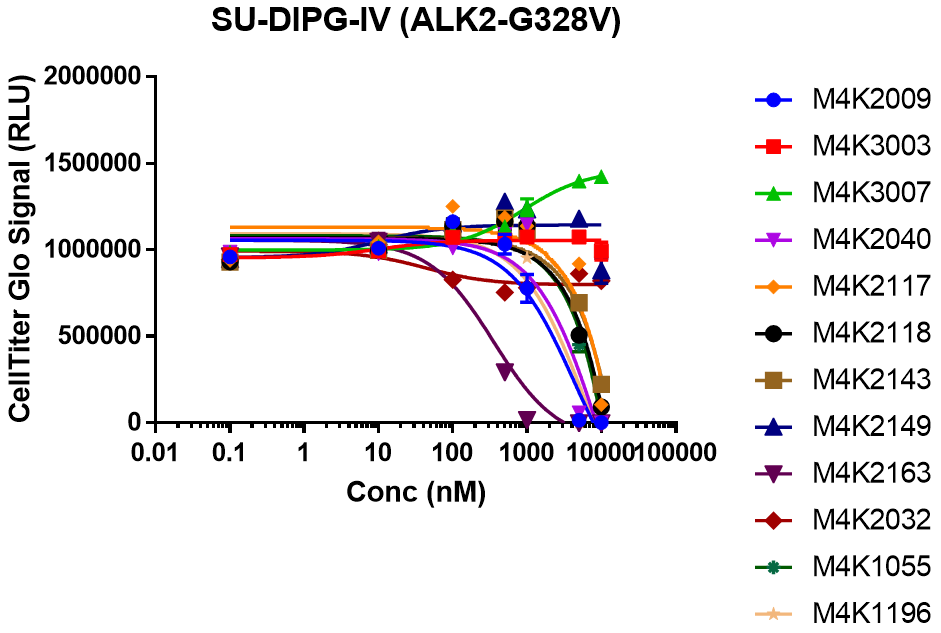
EC50 curves for SU-DIPG-IV cells treated with dilution series of each compound for 7 days.
Findings:
1) HSJD-DIPG-007 was sensitive toward most of the M4K compounds.
2) SU-DIPG-IV was not sensitive to most of the compounds.
3) M4K3003 and M4K3007 which were based on patent literature were not efficacious despite having decent potency towards ALK2.
4) M4K2009 was reduced the viability of DIPG lines with ALK2 mutation while M4K2163 showed efficacy in all of the DIPG cell lines.
In a nut shell:
More compounds still needs to be evaluated in more DIPG patient-derived cell lines in order to better establish relationship between ALK2 IC50, compound chemical structure and efficacy in reducing the viability of DIPG cells.
For detailed description of my experimental protocol, please refer to my Zenodo page.
