Hi,
I would like to share with you the details for cellular assay detecting interaction between histone deacetylase HDAC6 and ubiquitin, which is a unique property within the histone deacetylase family.
HDAC6 is a member of the histone deacetylase family which deacetylate lysine residues of histone and non-histone proteins. It plays an important role in a variety of cellular processes such as cell signaling, autophagy, and trafficking (PIMID:30176876, 22069321). HDAC6 is composed of two catalytic domains as well as a unique zinc-finger ubiquitin-binding domain (UBD). HDAC6 was shown to bind C-terminal RLRGG peptide present in ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like interferon (IFN)-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) via the UBD, which is an important step for misfolded proteins degradation (PIMID:29741882), autophagy, trafficking and other processes (PIMID:30176876, 22069321). By binding to polyubiquitinated or ISGylated protein aggregates and deacetylating tubulin, HDAC6 facilitates the transport of aggregates to the aggresome and their clearance by autophagy (PIMID:25429107, 22069321). HDAC6 interaction with ubiquitin and ISG15 was also shown to be important for viral infection as well as anti-viral defense. During the influenza A infection cycle, the virons fuse to late endosome membranes exposing a variety of unanchored ubiquitin moieties to the cytosol, attracting HDAC6 to the fusion site. HDAC6, in turn, binds to the capsid and links it to cytoskeleton motors dynein and myosin, generating a shearing force that disassembles the capsid allowing viral ribonucleoproteins to penetrate the cytosol (PIMID: 27783058). On the other hand, type I interferon pathway stimulation after viral infection leads to ISG15 expression and ISGylation of newly synthesized cellular and pathogenic proteins, which binds to HDAC6 leading to autophagic clearance (PIMID:25429107).
Summary
Assay measuring the interaction of HDAC6 UBD with ubiquitin is based on NanoBRET technology – a proximity-based assay that can detect protein interactions by measuring energy transfer from a bioluminescent protein donor to a fluorescent protein acceptor. Initially, we determined the optimal donor to acceptor ratio of donor construct: N-terminally NanoLuc® tagged HDAC6 or UBD and acceptor construct: N-terminally HaloTag®Fusion tagged ubiquitin and ISG15. Due to a much higher background in HDAC6/ubiquitin compared to HDAC6/ISG15 NanoBRET assay, possibly coming from protein polyubiquitination, the assay was initially optimized and validated based on HDAC6 and ISG15 interaction. After testing several cell lines and optimizing expression levels, the best results were obtained with MCF7 cells for UBD and with HEK293T for HDAC6. The assay was validated comparing the NanoBRET signal between wild type (WT) and ubiquitin/ISG15 binding deficient (R1155A, Y1184A) mutant (Mut) of HDAC6 and UBD. As shown in Fig 1. the NanoBRET ratios of ISG15 and Mut proteins were significantly lower compared to WT proteins. The assay was further validated with compound 135, the derivative of previously published UBD inhibitors (PIMID:29741882). Compound 135 antagonized HDAC6 and ubiquitin interaction in vitro with high potency (data not shown, Mandeep Mann) and decreased the NanoBRET ratio in a dose-dependent manner only in WT but not in Mut HDAC6 (Fig.2).
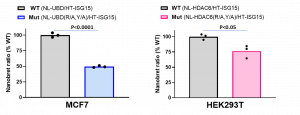
Fig.1. Mutation of R1155A and Y1184A in full length HDAC6 or UBD decreased interaction with ISG15– NanoBRET assay. MCF7 or HEK293T cells were co-transfected with N-terminally NL-tagged wild type or R115A, Y1184A mutant HDAC6-UBD or HDAC6, respectively, and N-terminally HT-tagged ISG15. The signal was read 48 h post transfection. Experimental triplicates of mean corrected NanoBRET ratios and t-test p values are indicated. NL – NanoLuc, HT– Halotag, Ub – ubiquitin.
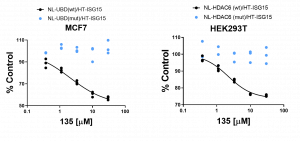
Fig.2. Compound 135 decreased the interaction of wild type but not binding deficient mutant of full length HDAC6 or UBD with ISG15 in a dose-dependent manner. MCF7 or HEK293T cells were co-transfected with N-terminally NL- tagged wild type or R115A, Y1184A mutant UBD or HDAC6, respectively, and N-terminally HT- tagged ISG15. The cells were treated with indicated compound 135 concentrations for 20 h. A. Compound 135 inhibited HDAC6-UBD and ISG15 interaction with IC50 = 2.1 µM. B. The compound135 inhibited HDAC6 and ISG15 interaction with IC50 = 2.2 µM. Experimental triplicates of mean corrected NanoBRET ratios presented as % of DMSO control are indicated. NL – NanoLuc, HT– Halotag.
We also optimized and validated the assay measuring the interaction between HDAC6 and ubiquitin. The biggest challenge of the assay was the high background possibly coming from unspecific interaction due to polyubiquitination and aggregation. To prevent possible protein aggregation, we shorten the assay to 24 h format. The new format was also tested and is recommended for UBD/HDAC6 and ISG15 NanoBRET assay. As shown in Fig 3. the NanoBRET ratios between ubiquitin and Mut proteins were lower compared to WT proteins, however, the statistical difference was only observed for HDAC6-UBD, not full HDAC6. We also looked at the effect of compound 987, the more potent derivative of compound 135, on HDAC6 interaction with ubiquitin in NanoBRET assay. Compound 987 decreased the NanoBRET ratio in a dose-dependent manner only in WT but not in Mut HDAC6-UBD or HDAC6 (Fig.4).
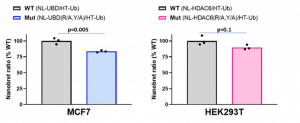
Fig.3. Mutation of R1155A and Y1184A in full length HDAC6 or UBD decreased interaction with ubiquitin – NanoBRET assay. MCF7 or HEK293T cells were co-transfected with N-terminally NL-tagged wild type or R115A, Y1184A mutant UBD or HDAC6, respectively, and N-terminally HT-tagged ISG15. The signal was read 24 h post-transfection. Experimental triplicates of mean corrected NanoBRET ratios and t-test p values are indicated. NL – NanoLuc, HT– Halotag, Ub – ubiquitin.
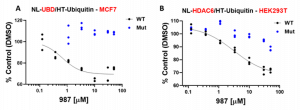
Fig.4. Compound 987 decreased the interaction of wild type but not binding deficient mutant of full length HDAC6 or UBD with ubiquitin in a dose-dependent manner. MCF7 or HEK293T cells were co-transfected with NL-tagged wild type or R115A, Y1184A mutant UBD or HDAC6, respectively, and HT-tagged Ub. The cells were treated with indicated compound 987 concentrations for 6 h. A. Compound 987 inhibited HDAC6-UBD and Ub interaction with IC50 = 0.7 µM in MCF7 cells. B. Compound 987 inhibited HDAC6 and Ub interaction with IC50 = 3.1 µM in HEK293T cells. Experimental triplicates of mean corrected NanoBRET ratios presented. The graphs represent non-linear fits of mean corrected NanoBRET ratios normalized to DMSO control. The experimental triplicates are indicated. NL – NanoLuc, HT– Halotag, Ub – ubiquitin.
For assay details, please go to Zenodo.
