Background
PRMT4 (CARM1) is type I protein arginine methyltransferase which mono- or asymmetrically dimethylates proteins (Fig.1) within proline-methionine rich motives, that are involved in transcription, splicing and RNA processing such as H3R17, EP300, PABP1, CA150, BAF155, MED12 (PIMID:19150423).
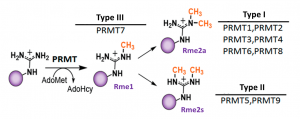
Fig.1. Mammalian PRMTs. There are 9 members and 3 types of the PRMT family. Type I, II and III PRMTs catalyze the formation of monomethyl arginines (Rme1). Type I PRMTs catalyze asymmetric arginine methylation (Rme2a), while type II PRMTs form symmetric arginine methylation (Rme2s). Type III PRMT can only monomethylate arginine residues. Modified from (PMID:29378138).
Assay validation
It has been reported that the RNA polymerase II mediator complex subunit 12 (MED12) and BAF155, are PRMT4 substrates (PIMID: 26601288, 25927994). Consistently with previous findings, PRMT4 knock-down decreased asymmetric dimethylation of MED12 and BAF155 (Fig.2). The assay was validated with PRMT4 selective chemical probe TP-064 (PIMID: 29719619). TP-064 decreased PRMT4 asymmetric dimethylation of MED12 (Z factor = 0.6) and BAF155 (Z factor = 0.76) in a dose-dependent manner (Fig.3).
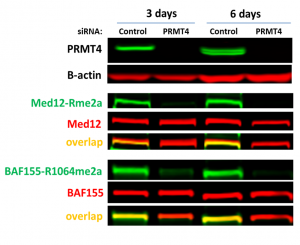
Fig.2. PRMT4 knock-down resulted in a decrease of MED12 and BAF155 asymmetric dimethylation (Rme2a) levels. HEK293T cells were treated with siRNA for 3 days and 6 days. The levels of methylation were analyzed in Western Blot.
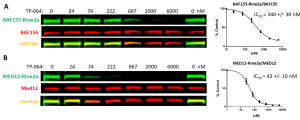
Fig. 3. TP-064 decreases PRMT4 dependent MED12 and BAF155 asymmetric dimethylation (Rme2a) levels. HEK293T cells were treated with PRMT4 selective inhibitor (TP-064) at indicated concentrations for 48 h and BAF155-Rme2a (A) and MED12-Rme2a (B) levels were determined by Western blot. The graphs represent nonlinear fits of methyl signal intensities normalized to total protein levels. The results are mean +/- SEM of 3 replicates.
Please go to Zenodo for experimental details.
