So I’m still ‘trying to catch them all’ as the young folks say (!) and building up my collection of purified GS loop mutations so that I can test them all together and start building up a picture of what phosphorylation sites are necessary for SMAD1 activation and which are not.
This time around I was aided ably by Jong Fu who was trying his hand at protein purification for the first time. I think (at least I hope!) you’ll agree he did a pretty good job!
The two mutants we were purifying this time were c108 and c133 which contain one and three mutations respectively. We were also purifying a fresh set of ACVR2A as the last test I did showed no SMAD1 activity (I’m going to write about this in the next blog post along with the follow-up experiment I did with this purification of ACVR2) but did show ACVR1 autophosphorylation suggesting the type I was active but something had happened to the type II protein to inactivate it.
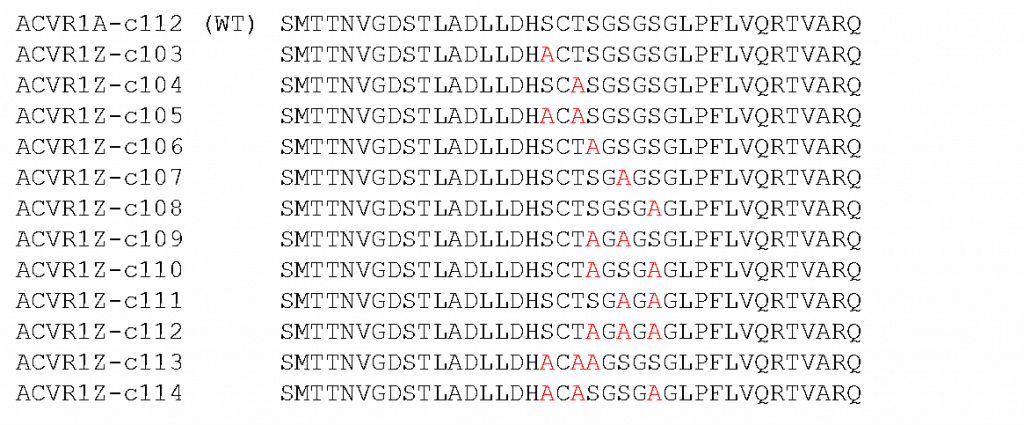
Fig. 1 – Showing the phospho-mutations introduced into the GS domain of ALK2.
This time around we also tried a slightly different method of purification using Talon resin bound to cobalt ions rather than using nickle – partly this was because our nickle resin was in a sorry state after many regenerations and partly this was because we’d got access to some cobalt talon resin from the membrane protein group who, because they require super clean resin for each purification, only use it once and then pass it onto other groups for use with higher expressing proteins.
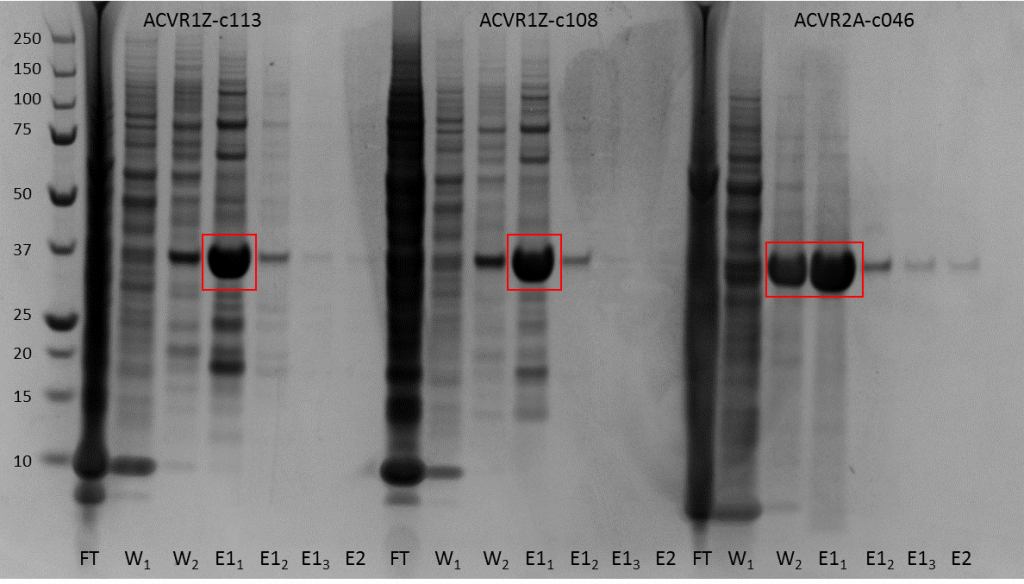
Fig. 2. SDS-PAGE gel of Talon column purification for all constructs showing flowthrough, washes and elutions. Boxed fractions have Tev added and taken on to gel filtration purification.
As you can see the talon resin worked out really well and we ended up with a really decent purification from it. The boxed fractions we cleaved overnight with Tev protease to remove the His tag and then concentrated them down to <5ml to purify on a GF75 size exclusion column.
This is shown in the gel below – in this case the boxed fractions are the ones chosen to be taken on for use in experiments – the other fractions, even though they contain the protein of interest, weren’t part of the main gel filtration peak and thus probably represent aggregates of the protein that we don’t want.
We then concentrated down the samples and froze them ready for future assays.
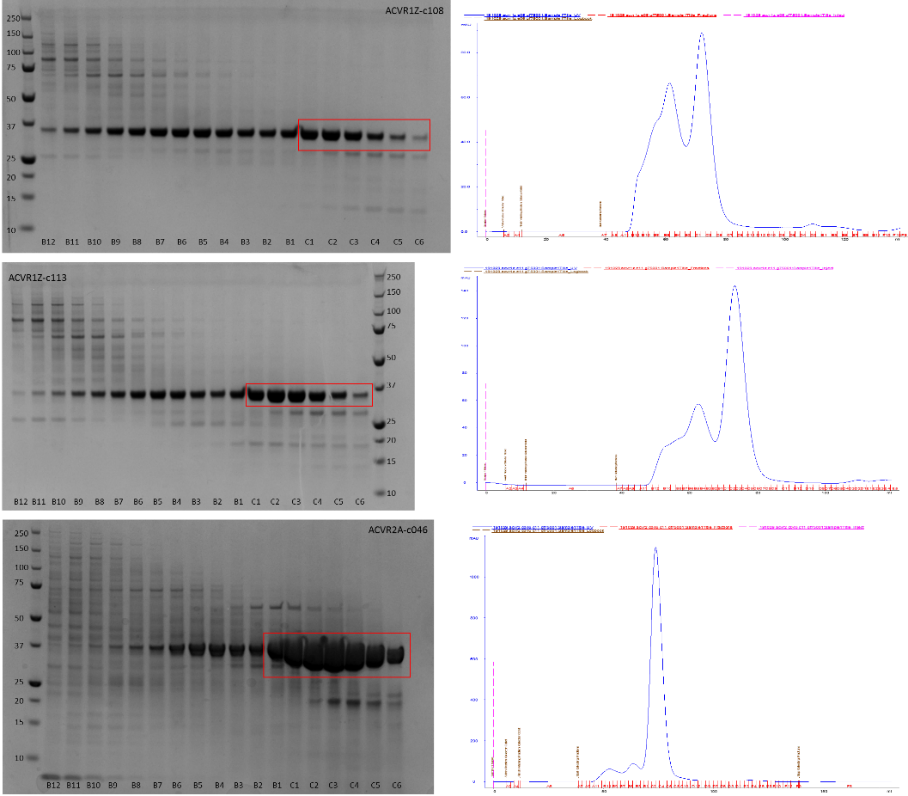
Fig. 3. SDS-PAGE gels (left) and akta traces (right) of the purification of ACVR1Z-c108, ACVR1Z-c113 and ACVR2A-c46 by size exclusion chromatography.
For full details on the purification you can head over to Zenodo and download the files.
