Hi all! Hope everyone is staying safe and practising social distancing during these difficult times. Working from home, I’ve decided to catch up on my open notebook.
In a previous post, I purified various full length USP5 constructs and determined the binding affinity of ubiquitin to these constructs. I wanted to determine the stoichiometry of ubiquitin (Ubq) binding to USP5, as USP5 has two ubiquitin-associated domains, in addition to its canonical zinc-finger ubiquitin binding domain (ZnF-UBD) and a cryptic ZnF-UBP domain (Figure 1)1.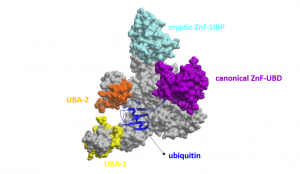
Figure 1. Schematic of full-length USP5 (grey) bound to ubiquitin (blue) (PDB: 3IHP): canonical ZnF-UBD (purple), cryptic ZnF-UBP (light blue), ubiquitin-associated domain-1 (yellow), ubiquitin-associated domain-2 (orange)
I used size exclusion chromatography-multiple angle light scattering (SEC-MALS) to determine the molar mass of the full-length USP5 protein in the presence and absence of an excess of monoubiquitin. MALS measures the light scattered by a protein at a range of angles allowing for extrapolation to determine molecular weight using a refractive index (RI) detector. Please see experimental details on Zenodo.
I looked at two full-length USP5 constructs: wildtype (WT) USP5, and an R221A mutant (this is a mutation at the canonical ZnF-UBD) in the presence and absence of ubiquitin (Figure 2 & 3). The molecular weight is summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Summary of Peak Molar Mass Moment and Molecular Weight
| Mp (g/mol) | Peak Molecular Weight (kDa) | |
| WT USP5 | 9.970 x 104 (±0.271%) | 99.7 |
| WT USP5 + Ubq | 1.068 x 105 (±0.338%) | 106.8 |
| R221A USP5 | 1.064 x 105 (±0.321%) | 106.4 |
| R221A USP5 + Ubq | 1.059 x 105 (±0.351%) | 105.9 |
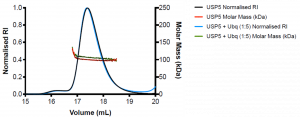
Figure 2. SEC-MALS of wildtype USP5 only (black) and wildtype USP5 + Ubq (blue)
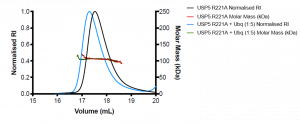
Figure 3. SEC-MALS of R221A mutant USP5 only (black) and R221A USP5 + Ubq (blue)
WT USP5 is fairly monodispersed (Mw/Mn= 1.1) and has a molecular weight of approximately 99 kDa, similar to the expected molecular weight of the protein which is 95.3 k Da. WT USP5 + Ubq elutes at the same volume as WT USP5 (17.4 mL) and has a molecular weight of approximately 107 kDa. This corresponds to 1:1 binding of ubiquitin (MW= 8.6 kDa) to USP5.
R221A USP5 has an approximate molecular weight of 106 kDa, which is higher than the expected molecular weight of the protein (MW= 99.6 kDa). R221A + Ubq also has an approximate molecular weight of 106 kDa. The mutant R221A ± Ubq are not significantly different and without orthogonal experiments, it is difficult to interpret what the MALS data means. Interestingly, there was a shift in the elution volume of the R221A + Ubq compared to R221A, where the R221A + Ubq elutes approximately 0.2 mL before R221A USP5. Perhaps, there is a conformational shift of the R221A USP5 in the presence of ubiquitin. Large conformational remodeling of full-length USP5 was previously suggested1.
Next, we will use dynamic light scattering (DLS) and small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) to better understand ubiquitin binding to various USP5 constructs, including R221A. Stay tuned!
1Biochemistry 2012, 51, 6, 1188-1198
