Background
PRMT3 is type I protein arginine methyltransferase which mono- and asymmetrically dimethylates proteins, mainly in glycine and arginine-rich motifs (Fig.1, PIMID: 15175657).
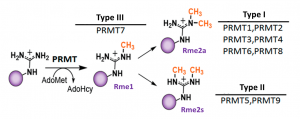
Fig.1. Mammalian PRMTs. There are 9 members and 3 types of the PRMT family. Type I, II and III PRMTs catalyze the formation of monomethyl arginines (Rme1). Type I PRMTs catalyze asymmetric arginine methylation (Rme2a), while type II PRMTs form symmetric arginine methylation (Rme2s). Type III PRMT can only monomethylate arginine residues. Modified from (PMID:29378138).
Assay validation
PRMT3 was shown to asymmetrically dimethylate histone H4 arginine 3 (H4R3) in vitro (PMID:22795084). Consistent with in vitro findings overexpression of wild type PRMT3 but not its catalytic mutant (E338Q) led to an increase in H4R3me2a (Fig.2). The assay was further validated with PRMT3 selective inhibitor SGC707, which decreased H4R3me2a levels in cells overexpressed with PRMT3 in a dose-dependant manner (Fig.3). The Z factor for the assay equals 0.59.
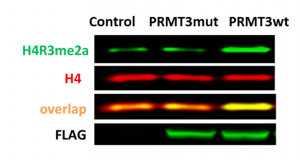
Fig.2. The wild type but not catalytic mutant (E338Q) of PRMT3 methylated endogenous H4R3. HEK293T cells were transfected with empty vector (control), FLAG-tagged PRMT3 wild type (PRMT3wt) or catalytic mutant (PRMT3mut) for 24 h. The methylation levels of H4R3 were analyzed in Western blot.
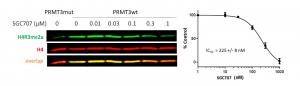
Fig.3. SGC707 decreases PRMT3 dependent H4R3 asymmetric dimethylation in cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged PRMT3 wild type (PRMT3wt) or catalytic (E338Q) mutant (PRMT3mut) and treated with PRMT3 selective inhibitor, SGC7070, for 20 h. H4R3me2a levels were determined by Western blot. The graph represents the nonlinear fit of H4R3me2a signal intensities normalized to total histone H4. The results are mean +/- SEM of 3 replicates.
Please visit Zenodo, for experimental details.
